Explainer: Multi-access Edge Computing
Trust in Digital Life Blog
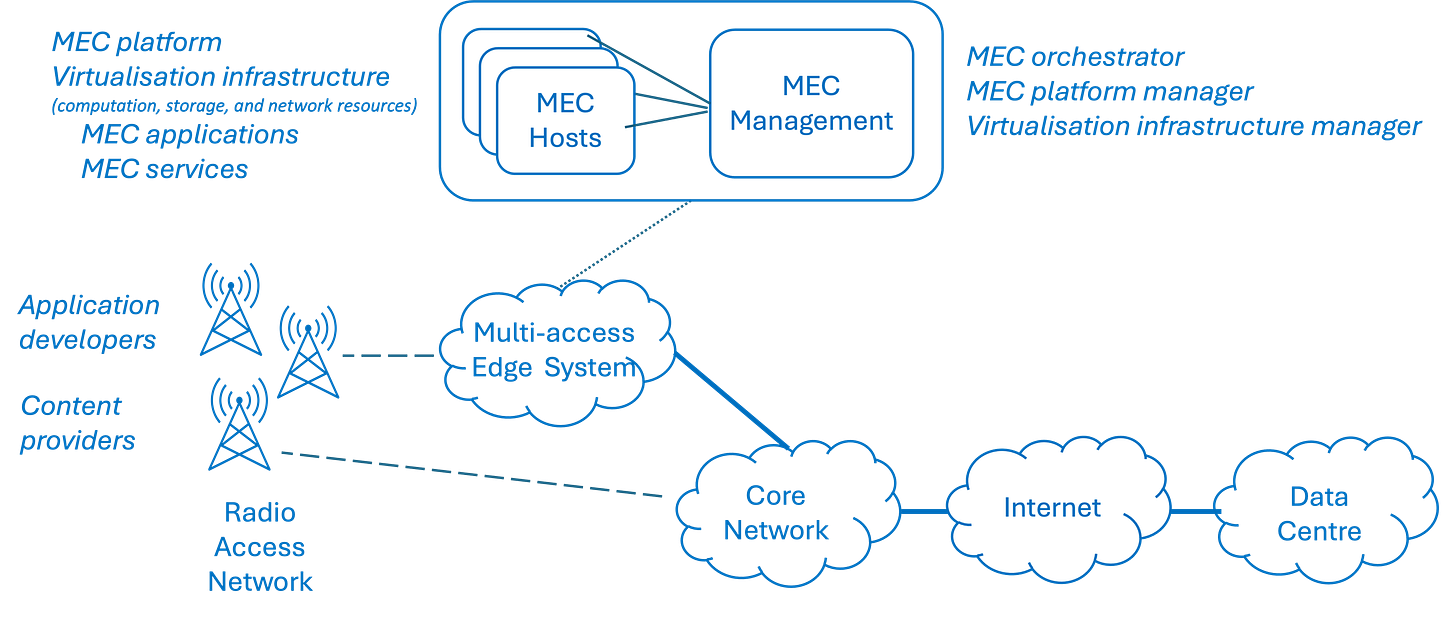
Multi-access edge computing (MEC), formerly referred to as mobile edge computing, is an ETSI-defined (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) network architecture concept that enables cloud computing capabilities and an IT service environment at the edge of a cellular network and more generally at the edge of any network, closer to end users, which significantly reduces latency and improves service delivery by processing data locally instead of sending it to a distant data centre. Essentially, it brings computing power closer to where data is generated, enabling faster response times for applications like augmented reality and real-time IoT data analysis.
MEC technology is designed to be implemented at the cellular base stations or other edge nodes and enables flexible and rapid deployment of new applications and services for customers. Combining elements of information technology and telecommunications networking, MEC also allows cellular operators to open their radio access network (RAN) to authorised third parties, such as application developers and content providers.
Key points about MEC:
• Low latency: The primary benefit of MEC is the ability to process data close to the source, minimising the time it takes for information to travel across the network, crucial for high bandwidth applications requiring immediate responses.
• Edge network placement: MEC servers are situated at the network edge, like cellular towers or local data centres, rather than in large, centralised data centres.
• Multiple access capabilities: "Multi-access" indicates that MEC can serve various types of devices simultaneously, including smartphones, IoT sensors and other connected devices.
Although MEC has only recently been proposed with the standards still being developed and only a handful of actual applications having adopted the architecture, the potential uses of MEC include:
• Autonomous vehicles: Real-time decision making based on local traffic conditions
• Augmented reality (AR): Processing visual data for immediate AR overlays
• Industrial automation: Monitoring and control of machinery in real-time
• Smart cities: Managing traffic flow and environmental data locally
The impact and importance of MEC systems will grow both with the advent of 6G and as more applications become virtualised and can be dynamically deployed, scaled and moved between the external cloud and the edge.